SQL Snippets
Overview
SQL snippets are reusable SQL fragments that can be used in queries across many reports, while having a single, central definition that can be updated easily.
A SQL snippet is defined as a name (e.g. my_snippet) and a replacement text, e.g. 'My sql snippet'
and referenced in the SQL queries or reports, filters or alerts with a square bracket notation, like this: SELECT [my_snippet].
When a SQL query needs to be started, all snippet references are replaced with the snippet text to get the complete SQL query to execute.
There are 2 categories of SQL Snippets:
- Built-in Snippets, which come with pre-defined behavior
- Custom Snippets, where you can freely choose the name and replacement text, optionally with parameters


Built-in Snippets
The built-in snippets allow a SQL query to take into account the user that is looking at the dashboard or the dashboard on which the report or dynamic filter is displayed.
The built-in snippets are:
| Snippet | Description |
|---|---|
[CLUVIO_USER_EMAIL] | The e-mail address of the logged-in user or NULL for sharing links or dashboards sent via dashboard schedule. |
[CLUVIO_USER_FIRSTNAME] | The first name of the logged-in user or NULL for sharing links or dashboards sent via dashboard schedule. |
[CLUVIO_USER_LASTNAME] | The last name of the logged-in user or NULL for sharing links or dashboards sent via dashboard schedule. |
[CLUVIO_USER_ROLE] | 'admin', 'analyst' or 'viewer' for logged-in users or NULL for sharing links or dashboards sent via dashboard schedule. |
[CLUVIO_DASHBOARD_NAME] | The name of the dashboard on which the report or dynamic filter is displayed. |
[CLUVIO_DASHBOARD_ID] | The ID of the dashboard on which the report or dynamic filter is displayed. |
Here is an example of such query:
SELECT [CLUVIO_USER_EMAIL], [CLUVIO_USER_FIRSTNAME], [CLUVIO_USER_LASTNAME], [CLUVIO_USER_ROLE],
[CLUVIO_DASHBOARD_NAME], [CLUVIO_DASHBOARD_ID]
The above query is executed in a dashboard context as:
SELECT 'user@example.com', 'John', 'Doe', 'viewer',
'Sample Dashboard', '69wx-3kz9-3opj'
Custom Snippets
Custom snippets allow defining a name and its replacement text freely.
Here is an example of a snippet definition and its usage:
Snippet name: with_us_airports
Snippet text:
WITH us_airports AS (
SELECT * FROM airports WHERE country='United States'
)
Report query:
[with_us_airports]
SELECT * from us_airports WHERE elevation > 1000
The above query is executed as:
WITH us_airports AS (
SELECT * FROM airports WHERE country='United States'
)
SELECT * from us_airports WHERE elevation > 1000
Snippets inside Snippets
A snippet replacement text can contain other snippets, with a limitation of:
- a maximum chain length of snippet references is 10 (i.e. snippet A using snippet B, which uses snippet C, etc.)
- no cycles in references (i.e. snippet A using snippet B, which uses snippet A)
Parameterized Snippets
A SQL snippet can optionally have parameters. To use snippet parameters, specify
the parameter names in the Params input field of the snippet editing dialog
(multiple parameter names are separated by a comma). Then use the parameter
names in the Text input for the snippet text by enclosing them in square
brackets (analogous to referencing another snippet).
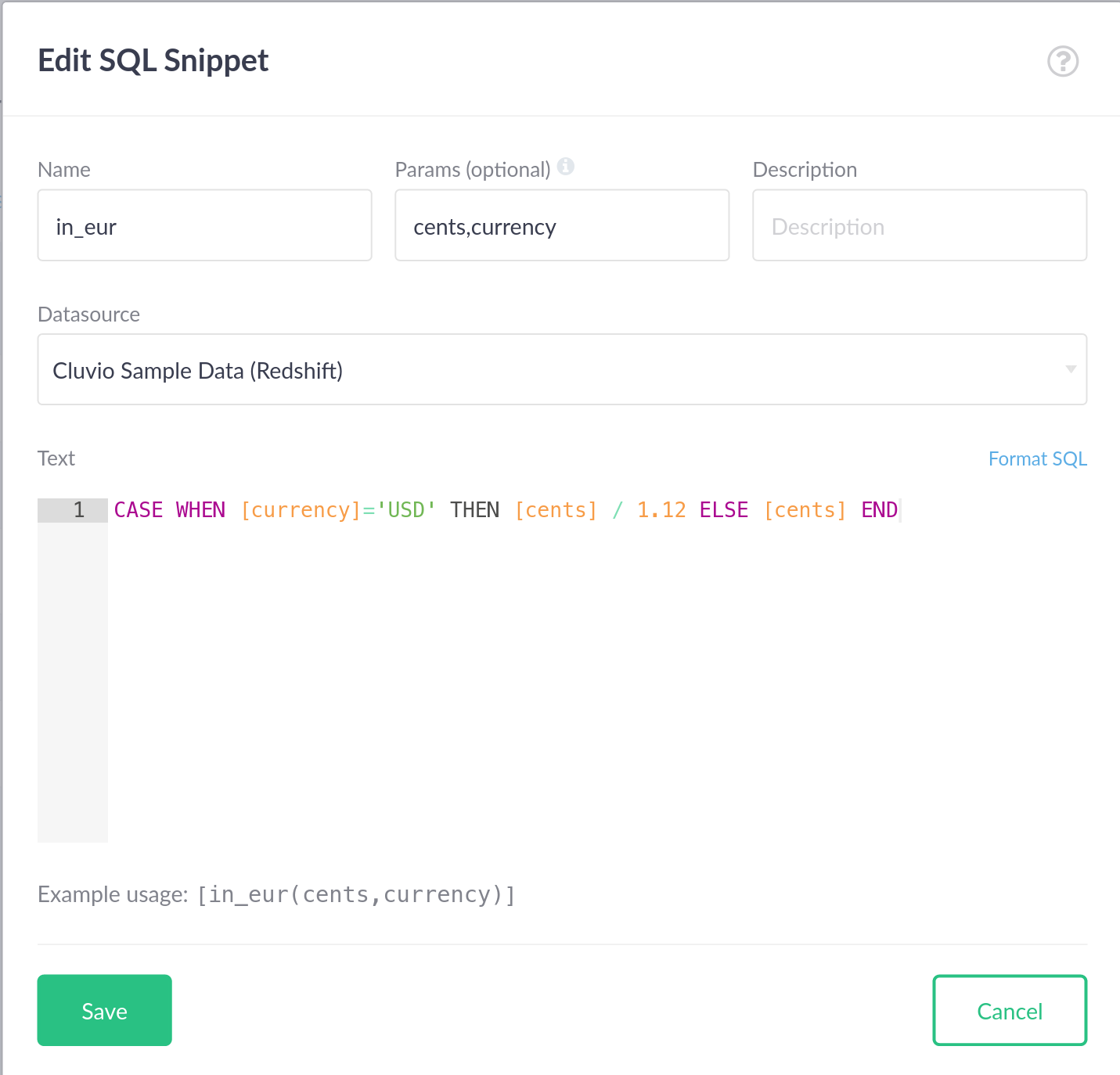
To use a parameterised snippet in a report, specify the parameters in brackets, analogous to a function call in a programming language:
SELECT [in_eur(100, 'USD')]
Any parameters that are defined by a snippet but are not passed when the snippet
is used will resolve to a literal NULL value in the resolved snippet text.
Managing Snippets
All custom SQL snippets defined for your organization can be managed from the
SQL Snippets overview page.


To create a SQL snippet, select Add SQL Snippet and specify its attributes in the modal dialog that appears.
Every SQL snippet must have a name, which is later used to reference the snippet
in a SQL query (e.g. of a report). The Datasource selection only influences code completion in the
SQL editor, but has no relevance for the actual use of the snippet.
The text of a snippet does not have to be a syntactically valid SQL query.
Usually, the snippet text is just a SQL fragment, which can be just a single literal value.
A SQL snippet can also be created directly from within the report SQL editor. See Report Editor → Creating Snippets.
To use a SQL snippet in a query, the snippet name is enclosed in square brackets, as in [my_snippet_name].
For example, if a snippet named revenue with the snippet text
SUM(price_paid) FROM sales WHERE order_type <> 'test_order'
is used in the SQL query
SELECT [revenue]
GROUP BY {saletime:month}
it expands upon query execution into
SELECT SUM(price_paid) FROM sales WHERE order_type<>'test_order'
GROUP BY {saletime:month}
Thus, snippets provide a central definition of frequently used SQL fragments and editing a snippet changes all report queries using that snippet. As a result, many similar queries can be shortened and become easier to maintain.
Snippets can reference other snippets. However, a chain of snippet references can be no more than 10 levels "deep" and must not contain cycles.
Report Editor
Auto-Completion
In the report SQL editor, snippets are included in the suggested auto-completions.


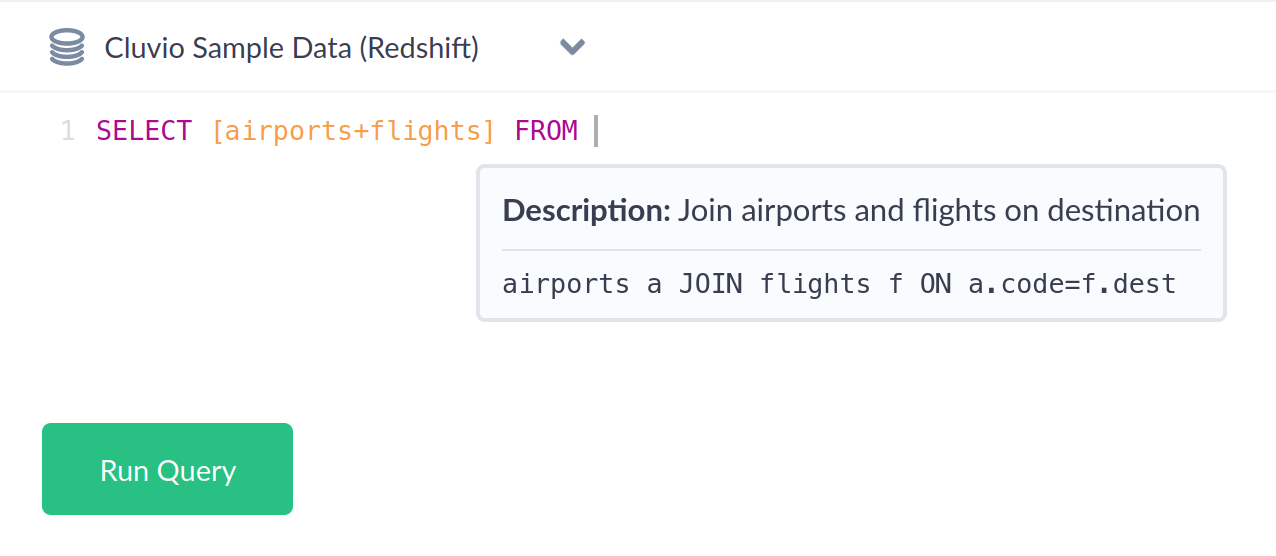
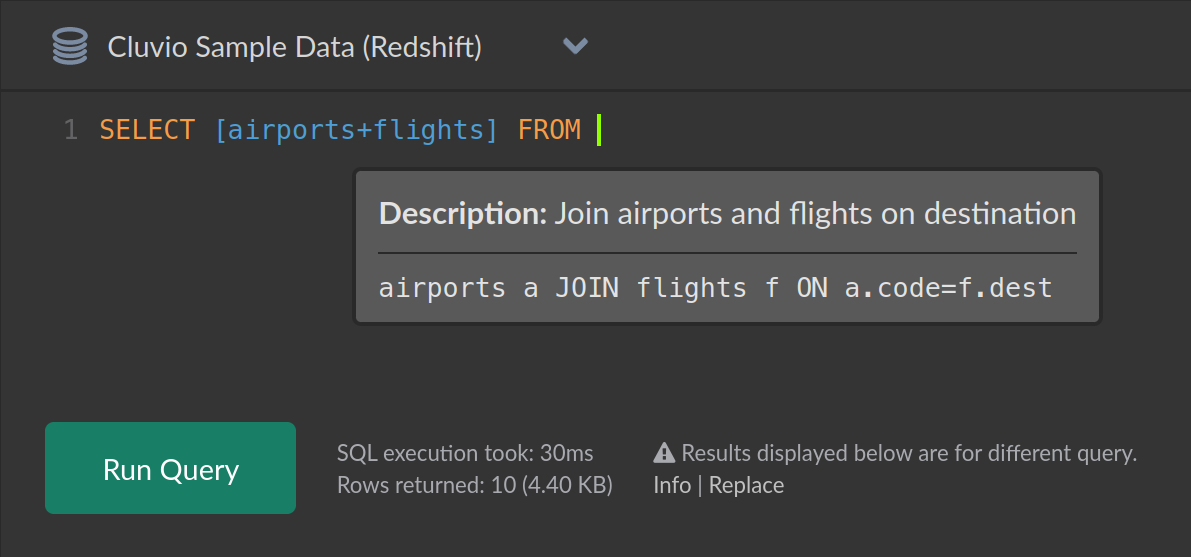
Snippet Tooltip
Hovering over a snippet in the report SQL editor opens a tooltip with the snippet text and description.
Creating Snippets
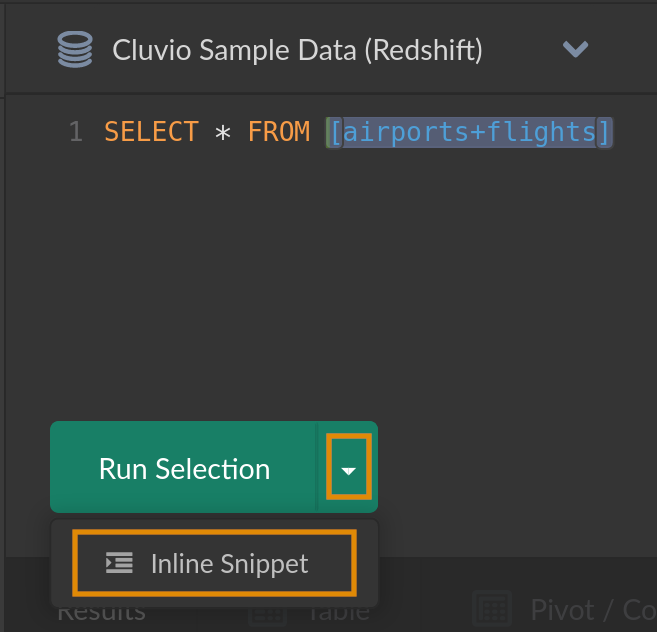
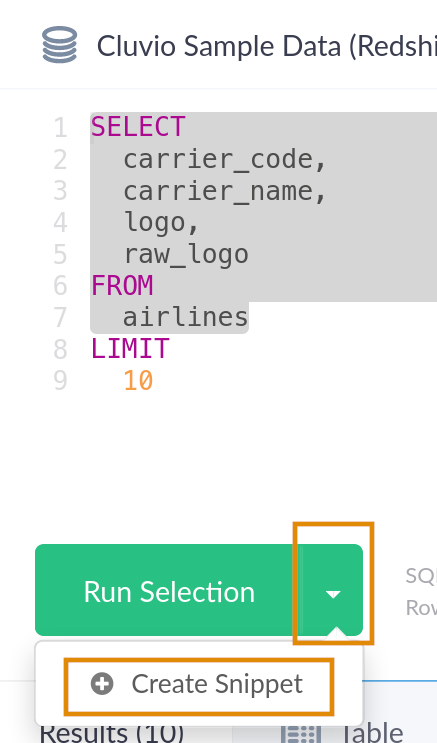
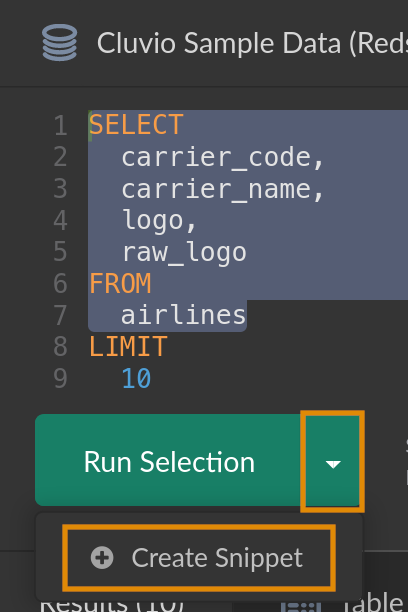
Snippets can also be created directly from within the report SQL editor.
To do so, select the portion of the SQL that you want to extract
into a snippet and choose Create Snippet from the editor's expanded Run-menu.
Inlining Snippets
A snippet reference can be inlined in the report SQL editor, e.g. to serve as a
template for further customization. To do so, select the snippet name (with or
without the surrounding square brackets) and choose Inline Snippet from the
editor's expanded Run-menu.